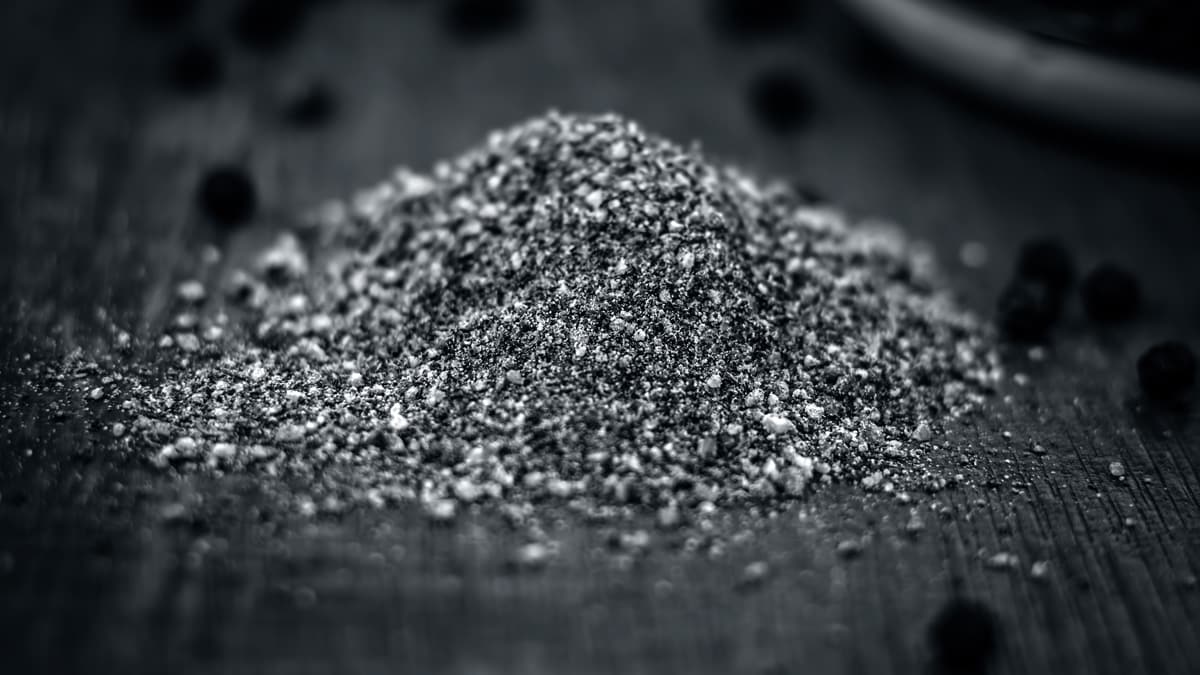
Tantalum powder is a gray-black or dark gray metal powder. Tantalum is a rare, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal known for its high melting point, excellent electrical conductivity, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and chemical environments. It is also biocompatible. There are three main types of tantalum powder: spherical, angular, and spherical. Each type has a unique physical shape and is derived from a unique process.
Spherical tantalum powder is produced by molten sodium reduction of tantalum salts or solid magnesium reduction of tantalum(V) oxide. Powders are mostly aggregates of particles and pores. It has relatively low density and high surface area.
Angular tantalum powder is produced by hydrogenation and crushing of solid ingots (electron beam or vacuum arc melting) and dehydrogenation. Particles appear angular and not agglomerated; generally higher packing density than spherical.
Spherical tantalum powder is produced by spheroidizing the above powder or wire. The particles produced by this manufacturing process have a nearly spherical shape with a smooth surface and a narrow particle size distribution. These properties play a key role in promoting excellent flow and achieving dense packing, making them ideal for 3D printing.

The Miracle of Tantalum
Tantalum, the star of the elements in tantalum powder, is a rare transition metal known for its remarkable properties. Let's take a closer look at what makes tantalum so extraordinary:
A. Excellent hardness:
Tantalum is one of the hardest materials on earth. Its exceptional hardness contributes to its durability and resilience, making it the first choice for harsh industrial environments.
B. Corrosion resistance:
Tantalum has unrivaled corrosion resistance. It can withstand the corrosive action of acids, making it invaluable in chemical and industrial applications.
C. High melting point:
Tantalum has a melting point of more than 3000 degrees Celsius and remains solid at extremely high temperatures, ensuring its stability under extreme conditions.
D. Excellent electrical conductivity:
Tantalum is an excellent conductor of electricity, making it an essential part of electronic devices and circuits.
E. Biocompatibility:
One of the outstanding characteristics of tantalum is its biocompatibility. This property makes it safe for use in medical implants and prosthetics.
Application of tantalum powder
Tantalum powder is widely used in various industries because of its excellent performance and diversified powder varieties:
A. Electronic products: Tantalum powder is an important part of manufacturing tantalum capacitors, which are used in electronic products such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. An integral part of the device.
B. Aerospace: The high melting point and corrosion resistance of tantalum powders make them indispensable in the aerospace industry, where they are used in aircraft and spacecraft.
C. Chemical Processing: The acid corrosion resistance of tantalum and its use in the form of spherical tantalum powder make it critical in chemical processing equipment.
D. Medical: The biocompatibility of tantalum makes it ideal for medical implants such as bone screws and dental devices.
E. 3D printing: The ability of spherical tantalum powders to promote excellent flow and dense packing has made them a popular material for additive manufacturing.
In summary
Tantalum powder is derived from the extraordinary properties of tantalum, which has become a versatile and valuable substance across multiple industries. Its exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, high melting point and biocompatibility pave the way for innovative solutions in electronics, aerospace, chemical processing, medical applications and even the exciting 3D printing fields. With the continuous advancement of technology, the application of tantalum powder is becoming more and more extensive.
Comments
0